Dust Flammability In this second part in our Series on Explosions and Flammability we will discuss Dust Flammability. The dust pentagon below shows that there are five (5) elements necessary for a dust deflagration to occur. Dust Flammability Pentagon Combustible dust Oxidant Ignition source Dispersion of dust Confinement of dust Although … [Read more...]
Hydrocarbon Gas Flammability – Part 1 of 3 in a Series on Explosions
Introduction to Hydrocarbon Gas Flammability Today in Part 1 we will introduce important concepts in hydrocarbon gas flammability. For a fire or deflagration to occur, three things must be present: oxygen (above the minimum oxygen of combustion), an ignition source, and hydrocarbons (in concentrations between the Upper Flammability Limit and Lower Flammability Limit). The … [Read more...]
Groundbreaking Fluorocarbon Chemical Conversion Technology Advances Under Montreal Protocol
Mini Refineries for Emerging Economies and Remote Locations
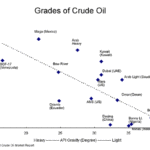
Modular mini refineries are best utilized in emerging economies and in remote locations where gasoline, diesel and fuel oil are needed. The local crude oil is normally your lowest cost feed stock because the transportation costs are minimized. Mini refineries with heavy crudes and low API gravity produce more fuel oil and less naphtha and diesel. Light crudes with high API … [Read more...]
The Chemistry and Physics of Rocket Engines
Propellants and oxidizers can be produced in modular plants near your rocket launch site. Chemical Propulsion The chemistry of traditional rocket engines is best described as combustion. Over the years many chemical systems have been used, which include but are not limited to: Propellent Hydrazine Highly Refined kerosene (RP-1) Liquid Hydrogen Highly … [Read more...]