Spinning Tube in a Tube Reactor
The STT ReactorTM reactor process helps substantially improve profits in chemical, petrochemical, biodiesel, pharmaceutical and bio-chemical operations through a paradigm leap from volume-based to area-based reaction systems. The STT® is one of the most important tools in a chemical engineers arsenal for creating smaller processes through process intensification.
Spinning Tube in a Tube - STT ReactorTM
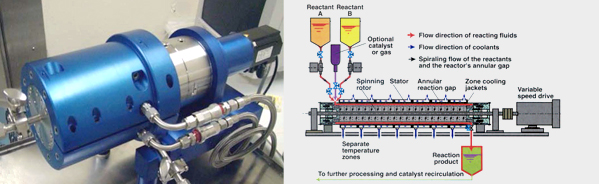
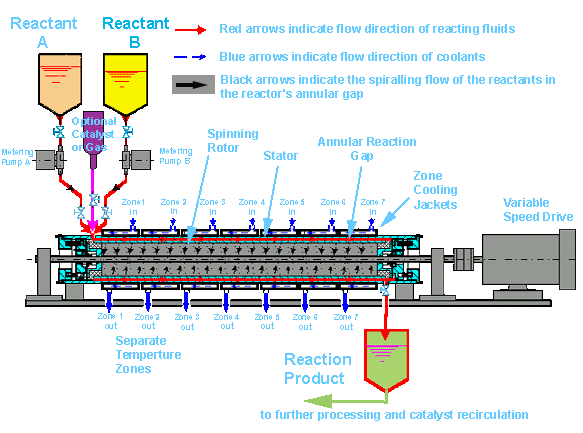
IntroductionThe STT ReactorTM process helps substantially improve profits in chemical, petrochemical, biodiesel, pharmaceutical and bio-chemical operations through a paradigm leap from volume-based to area-based reaction systems. STT Reactor TM BasicsBelow is a diagram of a typical STT Reactor TM. Reactant fluid A is instantaneously mixed with reactant fluid B in the STT ReactorTM with zero eddy decay. This can be accompanied with an optional gas or catalyst to complete or accelerate the reaction. The necessary residence time is controlled by the reactants' feed rates, as well as by the rotor speed. Separate temperature zones allow unprecedented temperature control of the reaction, including staging different temperature profiles for the complete reaction. The sub-Kolomogoroff eddies generated in the STT ReactorTM promote quick and efficient mixing of the reactants in a fraction of the time and power expended in conventional systems.
Why Is The STT ReactorTM Revolutionary?Process rates in reactors are influenced by the minimum length of turbulent eddies and the molecular-diffusive mixing time. The process rate time can be estimated using Einstein's diffusion equation:
The STT ReactorTM Reactor Process is capable of creating sub-Kolmogoroff and near-Kolmogoroff eddies and therefore can drastically reduce reaction time. The sub-Kolmogoroff eddies are possible through two dimensional containment of the fluid and zero eddy decay. Mixing power requirements and reaction time are drastically reduced compared to conventional reactors. How Does The STT ReactorTM Work?
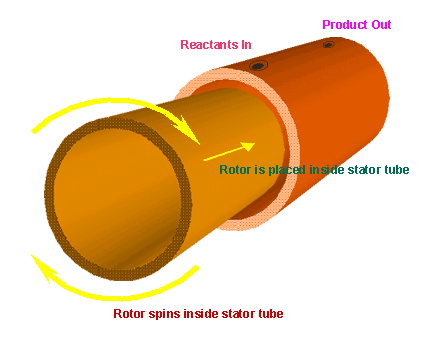
A tube is made to spin inside another tube, whereby only a very fine annular gap between the inner diameter of the outer tube and the outer diameter of the inner tube is maintained. This gap is concentric and is filled with the reactants. Immediately upon entry of the reactants, almost instantaneously a very large interfacial contact area is produced which is subject to extreme rates of surface renewal. Typical shear rate values are in the range of 30,000/sec. to 70,000/sec.
Advantages:Maximum Mass Transfer Rates
Maximum Heat Transfer Rates
Maximum Phase Interaction
Benefits: Benefits as a Result of the STT ReactorTM Geometry
Chemical Reactor Applications:
|
The STT ReactorTM is the Property of Brightpath
Please call for further information
R.C. Costello & Assoc., Inc.
1611 S. Pacific Coast Highway, Suite 302
Redondo Beach, CA 90277
Tel: (310) 792-5870, Fax: (310) 792-5877
E-MAIL: rcca[at]rccostello.com